The South China Sea
Political tensions are at high tide between nations

Map of the South China Sea
The Background
The South China Sea is one of the hottest topics debated today especially in terms of globalization and foreign affairs as it affects the whole world's economy. This area is home to many of the world's most important shipping routes and is currently being heavily contested for ownership by China. Some of the countries that have disputes over these claims are the United States, the Philippines, Vietnam, and Taiwan just to name a few. China has been aggressively pushing for more territory and monopolizing foreign trade with systems like the Belt Road Initiative and their South China Sea claims. China wants to control the whole sea basically to giving them full access to all the trade routes that run through here. This viewpoint is similar to the heartland theory where if they control the sea and exports they can control the whole world.
Video explaining the dispute
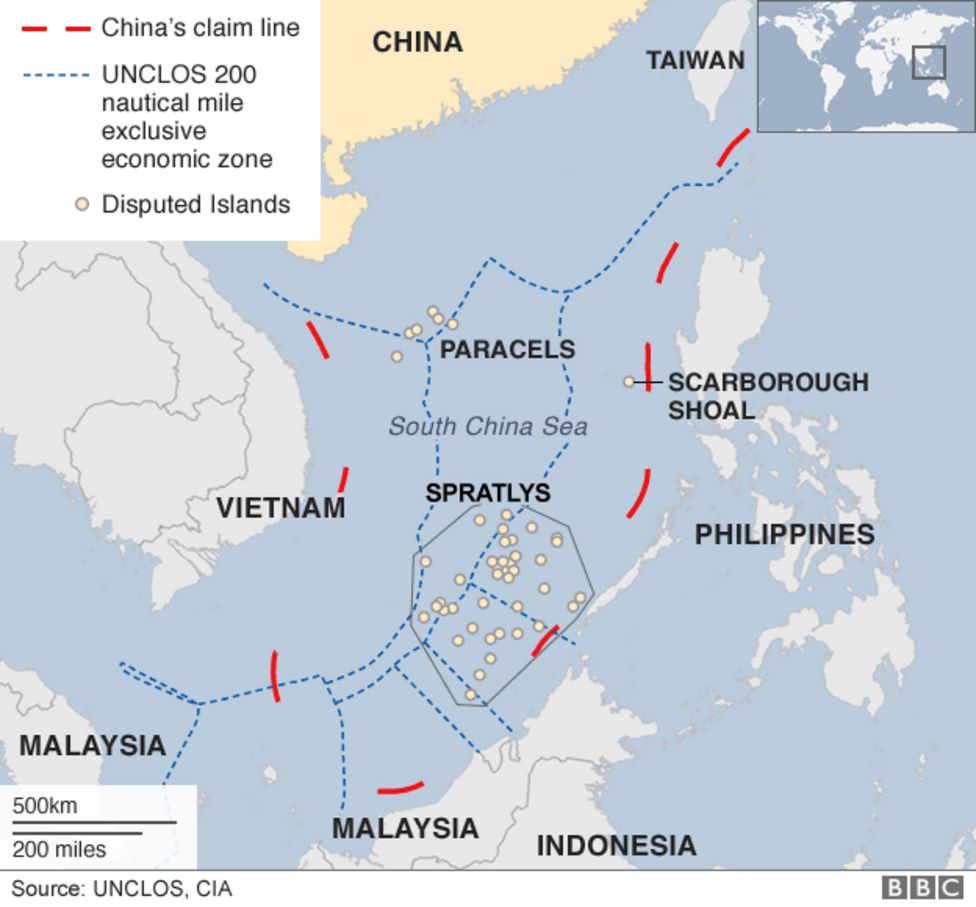
Map of China's claim marked by red-dashed line
What is Disputed?
According to an article by the BBC, "It is a dispute over territory and sovereignty over ocean areas, and the Paracels and the Spratlys - two island chains claimed in whole or in part by a number of countries. Alongside the fully-fledged islands, there are dozens of rocky outcrops, atolls, sandbanks, and reefs, such as the Scarborough Shoal" (BBC, 2016).
As you can see China's claim is marked by the red -dashed line on the image above and is clearly outside of the blue-dashed line which marks the UNCLOS 200 nautical mile economic exclusion zone. China is claiming to own the Spratlys and Paracels island chain which would allow them to have full fishing and trading rights within the islands.
Map of Waterways that feed into the Sea and the depth of the Sea itself
The Law of the Sea
According to an article written by Karan Chopra, "The law of the sea provides for full money rights to nations for a 200-mile zone by their shoreline. The sea and oceanic bed extending this area is regarded to be an Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and any country can use these waters for its economic utilization" (Chopra, 2021).
Under this clause from the Law of the Sea, China is heavily violating this international agreement that has been in effect since 1982 and would in turn invalidate all of China's claims to these islands. Most of the members of the UN have agreed that China's claims have no backing but this hasn't stopped China to start ramping up military operations in the area.
Artificial Island created by China in the South China Sea
China's Military Expansion
China has been rapidly increasing its naval and airforce presence over its claims and has started to even build its own islands as a result. These islands serve as military bases for ships or fighter jets to refuel while patrolling and protecting the claimed territories. This has resulted in altercations with the Philippines navy leading to high tensions between the close nations.
This aggression by the Chinese has alerted many of the nations not only in the South China Sea but also foreign superpowers like the US. This has led to the United Nations to denounce the actions taken by the Chinese and led many western powers like Australia to do the same.
Former Secretary of State Mike Pompeo
Western View on Dispute
According to an article by Poppy McPherson and Karen Lema, "'We are a battleground now,' Renato de Castro, an analyst with the Albert Del Rosario Institute for Strategic and International Relations in the Philippines, told Reuters by phone. 'It will be a long game.' A week ago, U.S. Secretary of State Mike Pompeo called Beijing’s claim to about 90% of the potentially energy-rich South China Sea 'completely unlawful' and accused Beijing of seeking a 'maritime empire'" (McPherson & Lema, 2020).
The US has led the way with the majority of western countries supporting this point of view on keeping the seas free and open. This is a noble cause but we must keep in mind that the US has many military bases in many different countries around the world and shouldn't be calling China a maritime empire when the US is arguably the closest thing to a modern day empire.
Trade Routes
The image above shows a huge reason why the Chinese want to control the South China Sea as it is quite literally the home of oil-exporting and importing routes. They would be able to cut off certain suppliers from the middle east from using this route and force tariffs on anyone using their waterways.
United States Influence
The image above displays the comparison of China's sphere of influence compared the United States sphere of influence and the number of US Military bases in the area. If anything this one of conveying who is really the 'Maritime Empire' within the South China Sea.
While the US influence is massive, it is also with good intention in making the trade routes free to all and keeping a check on China's growing military presence, and preventing them from bullying smaller nations out of the area.
Environmental Issues
China's massive claims have not only caused issues with economics but have caused huge environmental problems. The South China Sea is home to one of the most biodiverse ecosystems on the planet and is currently under threat due to massive drilling for oil and island-building used for military bases.
According to Chloe Houdre from Georgetown University, "The escalation of the conflict in the South China Sea has compounded these long-term problems in multiple ways. First, since 2013 five of the claimant-countries – led by China – have accelerated their efforts to build artificial islands in the South China Sea to claim sovereignty. China uses an especially harmful process to build these islands. Second, the conflict has caused claimant countries to encourage their people to fish with the goal of strengthening the territorial claims of these countries. The conflict has also made cooperation on fishery management more difficult. Third, the militarization of the South China Sea dispute has increased air and water pollution. Fourth, the conflict has encouraged claimant-countries to drill for hydrocarbons, which disrupts the ecosystem, causes pollution, and risks leaks" (Houdre, 2018).
South China Sea Dispute: Philippine military spots 'illegal' structures on reef | English World News
Extortion of resources
China has been exponentially increasing its manufacturing in the last 30 years and has run into a huge problem. The issue is where they are going to find all the necessary natural resources needed to sustain their huge factories. This one reason for the militarization of the South China Sea.
This huge area could provide China with even more access to natural gas and oil that could cut costs out of purchasing from a middle man like the middle east.
The South China Sea also is home to one of the world's biggest fishing hubs and provides many jobs and food to the Southeast Asian countries within the Sea.
Conclusion
I learned that the South China Sea is one of the most highly disputed topics in the world today and should be included in the talks of every political conversation involving foreign trade as it will set a precedent for the years to come depending on how the world handles it.
Human Geography has helped me understand the deeper connections within this highly disputed topic and gave me a new perspective on how to look at it instead of just right and wrong. It has also shown me how important it is to compare our position in the world to the other we are arguing against because that is how we can come to an understanding. The only way to come to a peaceful resolution in the South China Sea is to make compromises with each other diplomatically before it is too late and our worst fear of war becomes a reality.
Citations
- BBC. (2016, July 12). Why is the South China Sea contentious? BBC News. https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-pacific-13748349.
- BBC. (2020, July 25). South China Sea dispute: Australia says Beijing's claims have no legal basis. BBC News. https://www.bbc.com/news/worldaustralia-53536173.
- Benson, J. W. (2013, February 5). South China Sea: A History of Armed Conflict. USNI News. https://news.usni.org/2012/06/20/south-china-sea-historyarmed-conflict#:~:text=During%20the%201970s%20and%201980s,sunk%20or%20damaged%20beyond%20repair.
- Chopra, K. (2021, March 7). Nautical Law: What is UNCLOS? Marine Insight. https://www.marineinsight.com/maritime-law/nautical-law-what-is-unclos/.
- Council on Foreign Relations. (n.d.). Timeline: China's Maritime Disputes. Council on Foreign Relations. https://www.cfr.org/timeline/chinas-maritimedisputes.
- Hartman, L. (2019, July 11). The importance of the South China Sea. ShareAmerica. https://share.america.gov/importance-of-south-china-sea/.
- Houdre, C. (2018, July 12). Environmental Ramifications of the South China Sea Conflict: Vying for Regional Dominance at the Environment's Expense. Georgetown Law. https://www.law.georgetown.edu/environmental-law-review/blog/environmental-ramifications-of-the-south-china-sea-conflict-vying-forregional-dominance-at-the-environments-expense/.
- Jennings, R. (2020, January 1). A Year of Multiple Standoffs, Few Solutions in South China Sea Dispute. Voice of America. https://www.voanews.com/east-asia-pacific/year-multiple-standoffs-few-solutions-south-china-sea-dispute.
- Kaplan, R. D. (2016, February 6). The South China Sea will be the battleground of the future. Business Insider. https://www.businessinsider.com/whythe-south-china-sea-is-so-crucial-2015-2.
- LaFond, E. C. (n.d.). Economic aspects. Encyclopædia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/place/South-China-Sea/Economic-aspects.
- McPherson, P., & Lema, K. (2020, July 20). 'We are a battleground now': In Southeast Asia, U.S.-China tensions flare on social media. Reuters. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-usa-china-southeastasia-analysis/we-are-a-battleground-now-in-southeast-asia-u-s-china-tensions-flare-on-socialmedia-idUSKCN24L1TV.
- Ruwitch, J. (2020, July 13). U.S. Rejects Beijing's Maritime Claims In South China Sea. NPR. https://www.npr.org/2020/07/13/890464319/u-s-rejectsbeijings-maritime-claims-in-south-chinasea#:~:text=A%20Primer%20On%20The%20Complicated%20Battle%20For%20The%20South%20China%20Sea&text=In%202016%2C%20an%20inte rnational%20tribunal,the%20tribunal%20had%20no%20jurisdiction.
- Stashwick, S. (2019, August 19). China's South China Sea Militarization Has Peaked. Foreign Policy. https://foreignpolicy.com/2019/08/19/chinas-south-china-sea-militarization-has-peaked/.
- Thayer, C. (2020, July 28). Australia Abandons Its Neutrality on the South China Sea Maritime Disputes. – The Diplomat. https://thediplomat.com/2020/07/australia-abandons-its-neutrality-on-the-south-china-sea-maritime-disputes/.
- Understanding the South China Sea Dispute. Exclusive Commentaries on China-US Relations - CHINA US Focus. (n.d.). https://www.chinausfocus.com/south-china-sea/.
- United Nations. (n.d.). Overview - Convention & Related Agreements. United Nations. https://www.un.org/depts/los/convention_agreements/convention_overview_convention.htm#:~:text=by%20%22*%22.-,The%20United%20Nations%20C onvention%20on%20the%20Law%20of%20the%20Sea,the%20oceans%20and%20their%20resources.&text=The%20Convention%20was%20opened% 20for,1982%20in%20Montego%20Bay%2C%20Jamaica.
- US sanctions Chinese officials over Beijing's South China Sea activities. South China Morning Post. (2021, February 24). https://www.scmp.com/news/china/diplomacy/article/3117812/us-taking-additional-actions-south-china-sea-says-mike-pompeo.
- YouTube. (2021). South China Sea Dispute: Philippine military spots 'illegal' structures on reef | English World News. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4cGEY7XcvsA.
- YouTube. (2021). The Militarization of the South China Sea. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BHCkZbBwFyM.